[OpenGL]Foundations(Personal Sutdy Notes)
keywords: OpenGL, cookbook, basic knowledge, foundations, Personal Sutdy Notes
参考资料
OpenGL Reference Documentation
https://docs.gl/
OpenGL 4 Shading Language Cookbook, Second Edition
https://github.com/daw42/glslcookbook
Learn OpenGL
https://learnopengl.com/
opengl-tutorial
https://www.opengl-tutorial.org/
术语解释:
GLEW(OpenGL Extension Wrangler).GLM(OpenGL Mathematics)GLFWis an Open Source, multi-platform library for OpenGL, OpenGL ES and Vulkan development on the desktop. It provides a simple API for creating windows, contexts and surfaces, receiving input and events.
Shader类型
- vertex shader
- fragment shader(HLSL中叫做pixel shader,也是工业界的主流叫法)
- geometry shader
- tess_control shader
- tess_evaluation shader
- compute shader
OpenGL版本查询与设置
查询版本(使用glad的API):
GLint major, minor;
glGetIntegerv(GL_MAJOR_VERSION, &major);
glGetIntegerv(GL_MINOR_VERSION, &minor);
选择版本(使用glfw的API):
//OpenGL版本设置为4.6
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 4);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 6);
注意:设置版本号不得高于查询出来的版本号。
批量填充(populate)数据
OpenGL 4.0之前,比如要填充vertex数据,必须要逐个vertex设置。4.0之后,可以一次性填充一组vertex。
以填充position和color的vertex shader为例:
/////////////////// Create the VBO ////////////////////
float positionData[] = {
-0.8f, -0.8f, 0.0f,
0.8f, -0.8f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 0.8f, 0.0f };
float colorData[] = {
1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f };
// Create and populate the buffer objects
GLuint vboHandles[2];
glGenBuffers(2, vboHandles);
GLuint positionBufferHandle = vboHandles[0];
GLuint colorBufferHandle = vboHandles[1];
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBufferHandle);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 9 * sizeof(float), positionData, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBufferHandle);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 9 * sizeof(float), colorData, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// Create and set-up the vertex array object
glGenVertexArrays(1, &vaoHandle);
glBindVertexArray(vaoHandle);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0); // Vertex position
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1); // Vertex color
//break current vertex array object binding.
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBufferHandle);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (GLubyte *)NULL);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBufferHandle);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (GLubyte *)NULL);
glBindVertexArray(0);
多个Program切换
可以在一个OpenGL程序中创建多个Program对象(glCreateProgram创建),然后通过glUseProgram且切换使用需要的Program对象。
删除Program对象
如果一个Program对象不再使用,可以使用glDeleteProgram删除;如果这个Program正在使用,使用glDeleteProgram不会直接删除,而是给一个删除标记,等到下次OpenGL内部检测时才会删除。
删除一个Program对象后,会自动Detach之前Attach上去的所有ShaderObject(glCreateShader创建),但是不会删除这些ShaderObject,除非调用glDeleteShader。
动态获取 vertex input attributes
一般情况下,vertex输入属性是在shader代码中定义好的:
#version 410
layout (location=0) in vec3 VertexPosition;
layout (location=1) in vec3 VertexColor;
或者是在Program对象link之前(glLinkProgram),通过glBindAttribLocation来绑定索引:
//programHandle是已经创建好的Program对象
glBindAttribLocation(programHandle, 0, "VertexPosition");
glBindAttribLocation(programHandle, 1, "VertexColor");
那么有没办法在Program对象Link之后,再去查询获取vertex attributes的location等信息?方式如下:
//获取输入属性的个数
GLint numAttribs;
glGetProgramInterfaceiv(programHandle, GL_PROGRAM_INPUT, GL_ACTIVE_RESOURCES, &numAttribs);
//获取每个输入属性的名字、类型、索引
GLenum properties[] = {GL_NAME_LENGTH, GL_TYPE, GL_LOCATION};
printf("Active attributes:\n");
for( int i = 0; i < numAttribs; ++i )
{
GLint results[3];
glGetProgramResourceiv(programHhandle, GL_PROGRAM_INPUT, i, 3, properties, 3, NULL, results);
GLint nameBufSize = results[0] + 1;
char * name = new char[nameBufSize];
glGetProgramResourceName(programHandle, GL_PROGRAM_INPUT, i, nameBufSize, NULL, name);
printf("%-5d %s (%s)\n", results[2], name, getTypeString(results[1]));
delete [] name;
}
glGetProgramInterfaceiv、glGetProgramResourceiv、glGetProgramResourceName是OpenGL 4.3才提供的API。4.3之前的版本可以使用 glGetProgramiv、glGetActiveAttrib、glGetAttribLocation等接口来实现上述需求。
输出结果:
Active attributes:
1 VertexColor (vec3)
0 VertexPosition (vec3)
Uniform variables的意义和作用
前面介绍的 Vertex attributes 是一种通用的给 shader 填充输入参数的方式,Vertext attributes 在 shader 内部不仅可以被读取,还可以被修改。
但是 Uniform variables 在 shader 内只能被读取,如果要修改,必须在 shader 之外调用OpenGL的API。
什么情况下用Uniform variable:
在渲染一个模型时,由于其每个顶点(vertex)信息都不一样,所以每个顶点在调用 shader 时,shader 的输入参数都不一样,相当于每计算一个顶点,shader 的输入参数都得变化一次,针对这种实时变化的输入参数,最好使用 Vertex attributes ;对于像摄像机角度、投射变换(projective transformations)等数据,相对变化频率很低,这种情况下最好使用 Uniform variable,毕竟它在 shader 内为常量,所以编译器可以针对这种常量做优化来提升性能。
注意事项:
Uniform variables 可以定义在任何一个 shader 中,如果多个 shader 定义了名字相同的 Uniform variables,那么它们的类型也必须相同,也就是说:只要一处定义,就可以被当前程序的所有 shader 对象访问。
Uniform variables 常用的OpenGL API
假设测试的 uniform.frag 代码如下:
#version 410
layout (location = 0) in vec3 VertexPosition;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 VertexColor;
out vec3 Color;
uniform mat4 RotationMatrix;
void main()
{
Color = VertexColor;
gl_Position = RotationMatrix * vec4(VertexPosition,1.0);
}
那么OpenGL API获取并设置Uniform variables的方式如下:
rotationMatrix = glm::rotate(glm::mat4(1.0f), angle, vec3(0.0f,0.0f,1.0f));
GLuint programHandle = prog.getHandle();
//获取 Uniform variables 索引
GLuint location = glGetUniformLocation(programHandle, "RotationMatrix");
//通过索引获取 Uniform variables 的值
glUniformMatrix4fv(location, 1, GL_FALSE, &rotationMatrix[0][0]);
常用技巧:
-
如果要使用vec3作为 Uniform variables 类型,那么可以使用
glUniform3f或者glUniform3fv, 后缀带'v'的表示数组类型 。 -
通过数组索引访问 Uniform variables :
GLuint location = glGetUniformLocation( programHandle, "MyArray[1]" ); -
通过结构体成员变量访问 Uniform variables :
GLuint location = glGetUniformLocation( programHandle, "MyMatrices.Rotation" );
动态获取 Uniform variables
方式类似前面提到的动态获取 vertex input attributes,还是以前面的 uniform.frag 为例:
GLint numUniforms = 0;
glGetProgramInterfaceiv( handle, GL_UNIFORM, GL_ACTIVE_RESOURCES, &numUniforms);
GLenum properties[] = {GL_NAME_LENGTH, GL_TYPE, GL_LOCATION, GL_BLOCK_INDEX};
printf("Active uniforms:\n");
for( int i = 0; i < numUniforms; ++i )
{
GLint results[4];
glGetProgramResourceiv(handle, GL_UNIFORM, i, 4, properties, 4, NULL, results);
if( results[3] != -1 )
continue; // Skip uniforms in blocks
GLint nameBufSize = results[0] + 1;
char * name = new char[nameBufSize];
glGetProgramResourceName(handle, GL_UNIFORM, i, nameBufSize, NULL, name);
printf("%-5d %s (%s)\n", results[2], name, getTypeString(results[1]));
delete [] name;
}
OpenGL 4.3 之前的版本,则要使用:glGetProgramiv、glGetActiveUniform、glGetUniformLocation、and glGetActiveUniformName.
打印结果:
Active uniforms:
0 RotationMatrix (mat4)
Uniform blocks意义和作用
如果你的 OpenGL 程序中有多个 shader 对象,且这些 shader 使用了同一个 Uniform variables,而我们知道,Uniform variables的location等信息是在 shader 对象Link之后生成的,也就是说每当 Link 一个 shader对象时,这个Uniform variables 的location 可能发生变化(比如在 shader 对象A中,Uniform variables 的location 为1,shader 对象2中,那么Uniform variables 的location 为2,那么如果先link对象A,再link对象B,则这个Uniform variables的location对于 shader 对象A就已失效)。
所以需要一个管理当前Program对象中所有Uniform variables的管理器,这个管理器就是Uniform blocks。
使用实例:
以下代码是绘制一个同心圆渐变效果的 shader。
buniformblock.frag:
#version 430
layout (location = 0) in vec3 VertexPosition;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 VertexTexCoord;
out vec3 TexCoord;
void main()
{
TexCoord = VertexTexCoord;
gl_Position = vec4(VertexPosition,1.0);
}
basic_uniformblock.vert:
#version 430
in vec3 TexCoord;
layout (location = 0) out vec4 FragColor;
layout (binding = 1) uniform BlobSettings {
vec4 InnerColor;
vec4 OuterColor;
float RadiusInner;
float RadiusOuter;
} Blob;
void main()
{
float dx = TexCoord.x - 0.5;
float dy = TexCoord.y - 0.5;
float dist = sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
FragColor =
mix( Blob.InnerColor, Blob.OuterColor,
smoothstep( Blob.RadiusInner, Blob.RadiusOuter, dist )
);
}
OpenGL API 代码:
GLuint programHandle = prog.getHandle();
// Get the index of the uniform block
GLuint blockIndex = glGetUniformBlockIndex(programHandle, "BlobSettings");
// Allocate space for the buffer
GLint blockSize;
glGetActiveUniformBlockiv(programHandle, blockIndex,
GL_UNIFORM_BLOCK_DATA_SIZE, &blockSize);
GLubyte * blockBuffer;
blockBuffer = (GLubyte *) malloc(blockSize);
// Query for the offsets of each block variable
const GLchar *names[] = { "BlobSettings.InnerColor", "BlobSettings.OuterColor",
"BlobSettings.RadiusInner", "BlobSettings.RadiusOuter" };
GLuint indices[4];
glGetUniformIndices(programHandle, 4, names, indices);
GLint offset[4];
glGetActiveUniformsiv(programHandle, 4, indices, GL_UNIFORM_OFFSET, offset);
// Store data within the buffer at the appropriate offsets
GLfloat outerColor[] = {0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f};
GLfloat innerColor[] = {1.0f, 1.0f, 0.75f, 1.0f};
GLfloat innerRadius = 0.25f, outerRadius = 0.45f;
memcpy(blockBuffer + offset[0], innerColor, 4 * sizeof(GLfloat));
memcpy(blockBuffer + offset[1], outerColor, 4 * sizeof(GLfloat));
memcpy(blockBuffer + offset[2], &innerRadius, sizeof(GLfloat));
memcpy(blockBuffer + offset[3], &outerRadius, sizeof(GLfloat));
// Create the buffer object and copy the data
GLuint uboHandle;
glGenBuffers( 1, &uboHandle );
glBindBuffer( GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, uboHandle );
glBufferData( GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, blockSize, blockBuffer, GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW );
// Bind the buffer object to the uniform block
glBindBufferBase( GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, 1, uboHandle );
glBufferData的作用
Create the buffer object and copy the data into it:
GLuint uboHandle;
glGenBuffers( 1, &uboHandle );
glBindBuffer( GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, uboHandle );
glBufferData( GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, blockSize, blockBuffer, GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW );
The space is allocated within the buffer object and the data is copied when glBufferData is called.
glBindBufferBase的索引问题
glBindBufferBase函数参数的索引(第二个参数)必须与定义uniform时设定的layout(binding=)相同,例如:
glBindBufferBase(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, 0, uboHandle);
对应的uniform定义
layout (binding = 0) uniform BlobSettings {
vec4 InnerColor;
vec4 OuterColor;
float RadiusInner;
float RadiusOuter;
};
glBindBuffer与glBindBufferBase的区别
简述之:glBindBuffer 绑定的指针索引,是用来对 Buffer 填充或修改数据而使用的,但是这个索引无法作为输入参数传递给 shader ,如果要把这个索引传递给 shader ,那么必须使用glBindBufferBase。
书中原文:
You might be wondering why we use glBindBuffer and glBindBufferBase with GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER. Aren’t these the same binding points used in two different contexts? The answer is that the GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER point can be used in each function with a slightly different meaning. With glBindBuffer, we bind to a point that can be used for filling or modifying a buffer, but can’t be used as a source of data for the shader. When we use glBindBufferBase, we are binding to an index within a location that can be directly sourced by the shader. Granted, that’s a bit confusing.
uniform layout类型:
- std140
- shared
- packed
- row_major
- column_major
例如:
layout( std140 ) uniform BlobSettings {
};
多个修饰符可以组合使用:
layout( row_major, shared ) uniform BlobSettings {
};
fragment shader到vertex shader之间的工作流程(page 58)
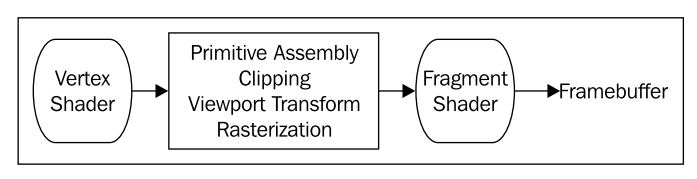
Between the vertex and fragment shader, the vertices are assembled into primitives, clipping takes place, and the viewport transformation is applied (among other operations). The rasterization process then takes place and the polygon is filled (if necessary). The fragment shader is executed once for each fragment (pixel) of the polygon being rendered (typically in parallel). Data provided from the vertex shader is (by default) interpolated in a perspective correct manner, and provided to the fragment shader via shader input variables. The fragment shader determines the appropriate color for the pixel and sends it to the frame buffer using output variables. The depth information is handled automatically.
Attribute vs Uniform vs Varying
- const – The declaration is of a compile time constant.
- attribute – Global variables that may change per vertex, that are passed from the OpenGL application to vertex shaders. This qualifier can only be used in vertex shaders. For the shader this is a read-only variable. See Attribute section.
- uniform – Global variables that may change per primitive […], that are passed from the OpenGL application to the shaders. This qualifier can be used in both vertex and fragment shaders. For the shaders this is a read-only variable. See Uniform section.
- varying – used for interpolated data between a vertex shader and a fragment shader. Available for writing in the vertex shader, and read-only in a fragment shader. See Varying section.
Origin: differences between an attribute, a uniform, and a varying variable
https://stackoverflow.com/a/17557438/1645289
OpenGL耗时较高的函数
glBufferData()
glBufferSubData()
glCompressedTexImage2D() / glCompressedTexImage3D()
glCompressedTexSubImage2D() / glCompressedTexSubImage3D()
glTexImage2D() / glTexImage3D()
glTexSubImage2D() / glTexSubImage3D()
glcompileshader() / glshadersource()
gllinkprogram()
如何限制帧率
你写一个简单的hello triangle,GPU占用接近100%,大概率是没有限制刷新率(即没有开启垂直同步VSync)。
在glfwMakeContextCurrent(wnd);之后追加glfwSwapInterval(1):
glfwSwapInterval(1): the application should run at <= refresh rate (display hardware).glfwSwapInterval(0): the application can run at any rate, and should run faster than withglfwSwapInterval(1).
Windows下若启用了DWM(Desktop Window Manager, also named Desktop Composition),此时使用glfwSwapInterval(1)开启VSync无效。
解决办法:
GLFW提供了cmake的define编译选项GLFW_USE_DWM_SWAP_INTERVAL,表示即使使用DWM或Windows Aero,也强制开启VSync。
Origin:
https://discourse.glfw.org/t/i-have-a-question-about-fps/1498
https://stackoverflow.com/a/16303811/1645289
gl_Position (Homogeneous coordinates)
What can I do with the 4th component of gl_Position?
https://gamedev.stackexchange.com/a/153137/117871
如何通过UV获取纹理采样中的像素
vertex shader
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aColor;
layout (location = 2) in vec2 aTexCoord;
out vec3 ourColor;
out vec2 TexCoord;
void main()
{
gl_Position = vec4(aPos, 1.0);
ourColor = aColor;
TexCoord = aTexCoord;
}
pixel shader
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec3 ourColor;
in vec2 TexCoord;
uniform sampler2D ourTexture;
void main()
{
FragColor = texture(ourTexture, TexCoord);
}
Origin: Texture https://learnopengl.com/Getting-started/Textures
sampler2D texture
The sampler2D is bound to a texture unit. The glUniform call binds it to texture unit zero. The glActiveTexture() call is only needed if you are going to use multiple texture units (because GL_TEXTURE0 is the default anyway).
Origin: https://stackoverflow.com/a/10869118/1645289
Layered rendering (Layered Images)
AMD RGP统计数据中有个叫Shaded GS primitives的属性,其统计来源自cube-based shadow mapping(比如point light的shadow map),而cube-based shadow mapping是通过Layered rendering来实现。
Layered rendering
https://www.khronos.org/opengl/wiki/Geometry_Shader#Layered_rendering
Layered Images
https://www.khronos.org/opengl/wiki/Framebuffer_Object#Layered_Images
Texture Image Units (Max limits)
int total_units;
glGetIntegerv(GL_MAX_COMBINED_TEXTURE_IMAGE_UNITS, &total_units);
std::cout << total_units << '\n'; // the result is 192
int vertex_units, fragment_units;
glGetIntegerv(GL_MAX_VERTEX_TEXTURE_IMAGE_UNITS, &vertex_units);
std::cout << vertex_units << "\n"; // the result is 32
glGetInteferv(GL_MAX_TEXTURE_IMAGE_UNITS, &fragment_units);
std::cout << fragment_units << "\n"; // the result is also 32
What is GL_MAX_COMBINED_TEXTURE_IMAGE_UNITS?
https://gamedev.stackexchange.com/a/192160/117871
莫道不消魂?帘卷西风,人比黄花瘦。---李清照《醉花阴》